A spherical mirror is characterized by its radius of curvature R. In the case of spherical mirrors there is only one focal point F = F '= R / 2 whose position coincides with the midpoint between the center of the mirror and the vertex thereof. Will be on the left of the vertex to the concave mirrors and convex mirrors right.
Increased mirror will be A = y '/ y depends on the curvature of the mirror and the position of the object.
The construction of images is very easily done using the main beams:
• Parallel Ray: Ray optical axis parallel to the upper part of the object. Refracted after passing through the image focus. • Lightning focal
: Ray from the top of the object and passes through the focal object, which is refracted in a way that goes parallel. Refracted after passing through the image focus.
• Radial Ray: Ray from the top of the object and is directed toward the center of curvature of the diopter. This beam is not refracted and continues in the same direction as the angle of incidence is zero.
MAIN ELEMENTS OF SPHERICAL MIRRORS
1) Center of curvature (C): In a spherical mirror is the center of the sphere it belongs to the optical surface
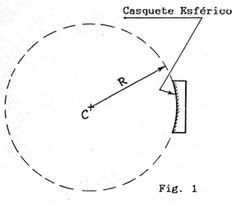
2) Radio curvature (R): In a mirror is the radius of the sphere.
3) Optical axis: the line is determined by the center of the disk mirror, called vertices (V) and its Center of Curvature (C)
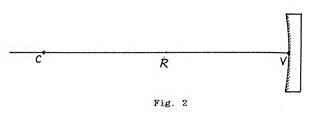
4) Main Focus (F): The point at which converge the rays reflected by the mirror, when it impinges on a beam parallel to its optical axis
. The main focus located on the optical axis, equidistant from V and ofC.
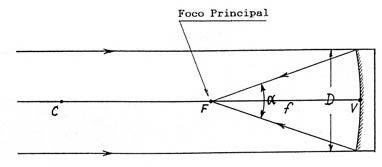
5) Aperture: The opening line is the diameter (D) of the mirror. The opening angu1ar (a) is the angle with vertex at the focus F whose sides pass through the ends of a diameter.
6) Focal Length (f): The distance between the vertex V of the mirror and its focus F. Turns out to be f = R / 2.
7) focal ratio (f): the ratio between focal length f and diameter D of the mirror: F = f / D.
8). Focal Plane: The plane perpendicular to the optical axis passing through the principal focus F.
9) Arrow (j): It is the small segment between the vertex and the midpoint of an optical diameter of the mirror.

0 comments:
Post a Comment